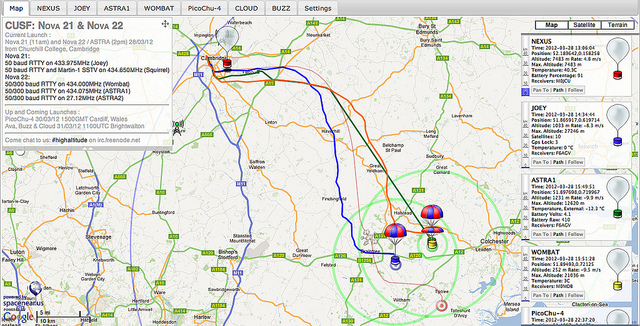
Joey-M Flight Computer
A baby Wombat
A lightweight, low power, compact, frequency agile HAB flight computer. Designed and built for CU Spaceflight in 2012/2013.
Joey-M uses the uBlox NEO-6Q GPS with a Sarantel SL1202 passive antenna, along with a small I2C EEPROM such that configuration can be retained when Joey is powered off. USB is broken out to a Micro USB connector such that configuration and debugging can be achieved via the excellent u-Center software from uBlox, and the configuration saved to EEPROM.
Joey-M uses the Micrel MICRF112 434MHz ISM band 10mW FSK transmitter with a twin varactor diode crystal pulling arrangement. Its 13.56MHz crystal has an 18pF capacitor on one side, and the varactor arrangement designed such that under no bias voltage, it also rests at 18pF.
One varactor has a large range of capacitance that allows the center radio frequency to be moved around by about 30kHz. The other varactor has a much smaller range, such that it can be used for very small shifts for FSK. Voltage is applied to the varactors by a twin 16 bit DAC from Linear Technology.
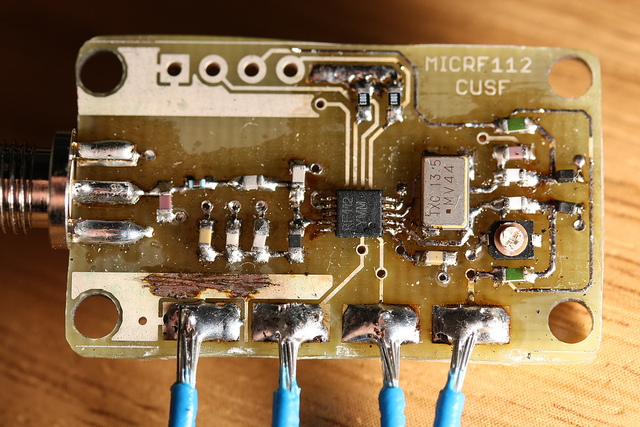
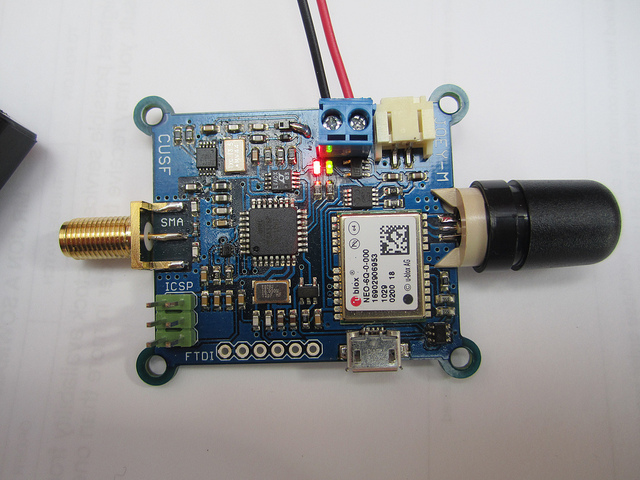
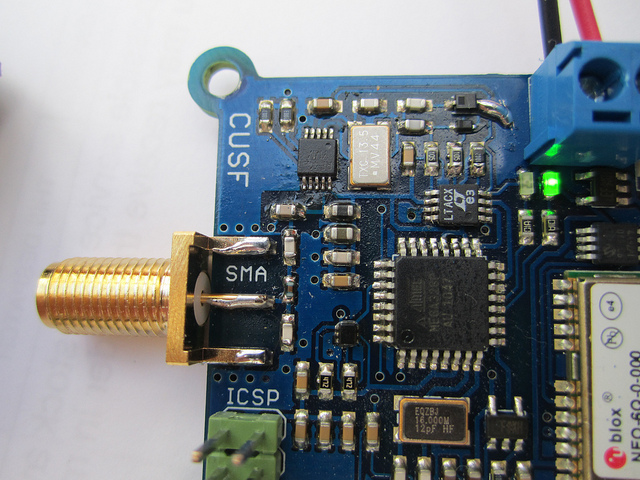
The revision 2 (R2) hardware fixes several bugs in the R1 firmware including incorrect grounding of the varactor diodes. A batch of 12 boards was manufactured in order that a simple, lightweight tracker should always be available whenever required at short notice.
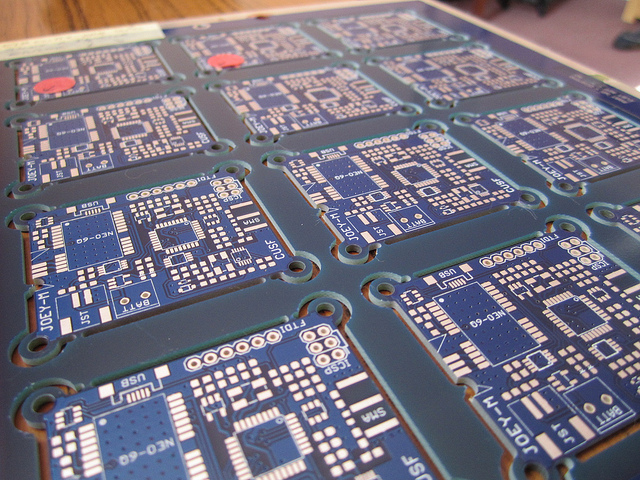
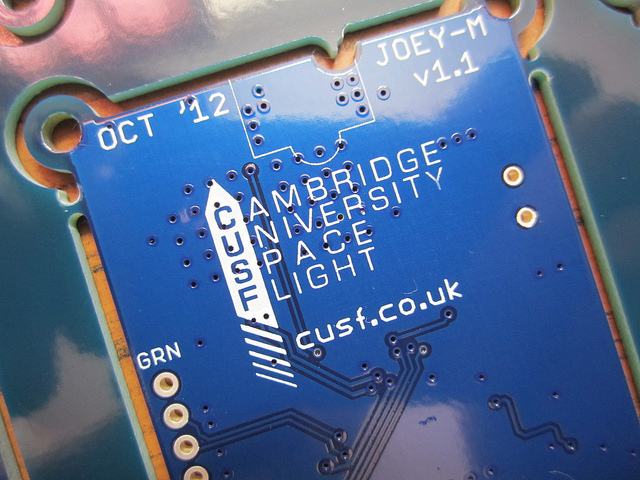
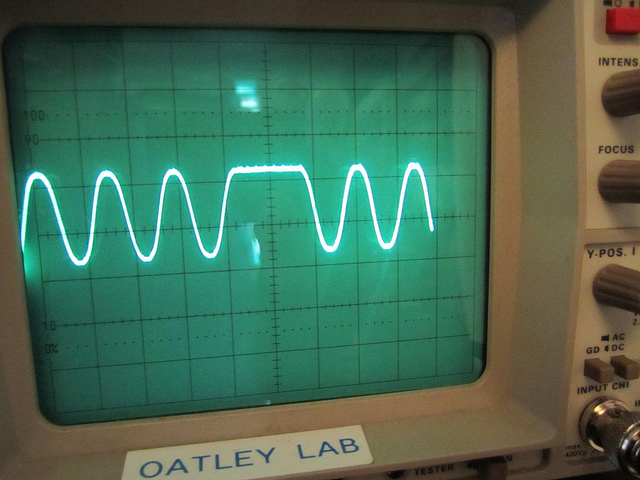
To ensure a clean spectrum and thereby increasing the ability to decode, the modulator input waveform is digitally filtered in a Gaussian shape to provide GFSK. The step response of the order-50 Gaussian filter is stored in EEPROM on the AVR, and is written out to the DAC on each change of modulator input voltage.